Cloud Sprawl
What Is Cloud Sprawl?
Cloud sprawl refers to the uncontrolled growth of cloud resources such as compute instances, storage, identities, services, containers, and SaaS applications across multiple accounts and environments.
Organizations launch new workloads, storage, identities, and services to keep projects moving and deliver faster outcomes. Over time, those quick decisions accumulate! Resources are created across accounts, regions, and cloud providers, but few are revisited, standardized, or retired. What begins as flexibility slowly turns into complexity.
The unchecked expansion of cloud resources leads to cloud sprawl. It thrives in environments where visibility is fragmented, ownership is unclear, and governance cannot keep pace with growth. As cloud sprawl spreads, organizations lose a clear understanding of what exists in their cloud, who owns it, and whether it is secure, compliant, or even still needed.
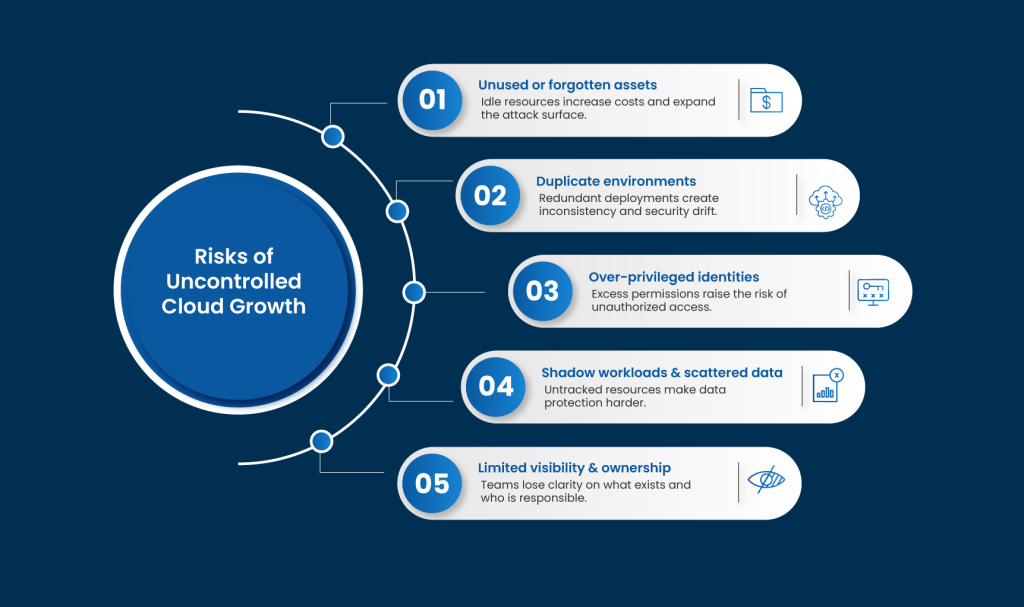
Why does Cloud Sprawl Happen?
Cloud sprawl often emerges due to the drive for speed in modern organizations, where rapid cloud adoption outpaces centralized control. As teams independently use self-service provisioning to launch cloud services and virtual machines, resources grow without consistent oversight from IT, security, or governance teams.
Some of the reasons are as follows:
- Uncontrolled Resource Provisioning
Cloud environments make it easy to launch resources in minutes. Teams create VMs, containers, databases, and test environments to solve immediate problems, but teardown rarely follows. Without clear controls, temporary setups remain active, increasing costs, expanding the attack surface, and introducing long-term security risks. - Shadow IT and Independent Teams
Developers and business units often adopt cloud services outside approved workflows to move faster. While this boosts agility, it also creates workloads that security teams are unaware of. These hidden assets lack monitoring, policy enforcement, and patching, instantly creating blind spots that attackers can exploit. - Multi-Cloud Complexity
Managing multiple cloud providers leads to limited visibility. Each platform has its own dashboards, security controls, and policy models. Managing them in silos makes it difficult to enforce consistent configurations, track assets centrally, or identify misconfigurations that span environments. - Poor Tagging and Ownership Gaps
When resources are not properly tagged with owner, purpose, or environment, accountability disappears. Teams move on, projects end and assets are forgotten. These orphaned resources continue running, consuming budget and remaining exposed, with no clear owner to secure or retire them. - Alert Noise Overload
Cloud security tools generate a high volume of alerts, many of which are low risk or lack context. Security teams spend time sorting through noise instead of fixing critical issues. As a result, high-impact misconfigurations and exposures can remain unnoticed and unresolved for long periods. - Cost Overruns
Idle virtual machines, orphaned storage volumes, forgotten test environments, and duplicated services silently consume budget. These resources continue to generate costs long after their business purpose has ended, making cloud spend unpredictable and difficult to optimize. - Security Weaknesses
Every unmanaged asset becomes a potential entry point. Unpatched systems, misconfigured services, exposed storage, and overly permissive identities expand the attack surface—often without security teams even realizing these resources exist. - Compliance Challenges
Sprawling environments make it harder to enforce consistent controls for encryption, access management, logging, and data residency. This increases the risk of audit failures, regulatory penalties, and loss of customer trust. - Operational Overhead
Fragmented cloud environments demand more manual effort for patching, audits, incident response, and lifecycle management. Teams spend valuable time reacting to issues instead of proactively improving cloud hygiene. - Visibility Gaps
Without a unified view, organizations struggle to answer basic questions: What resources are running? Who owns them? Are they secure and compliant? These blind spots slow decision-making and increase risk.
Having identified why cloud sprawl occurs, it is important to apply the right controls to limit operational, security, and governance risks
How to Control and Prevent Cloud Sprawl
Cloud sprawl can be effectively managed when organizations adopt a proactive, automation-driven approach that balances governance with agility, enabling teams to innovate and scale efficiently while maintaining control over their cloud environments.
This balance is best achieved by putting the right structure in place, starting with clear ownership and standardized practices, such as:
- Establish a Cloud Centre of Excellence (CCoE)
A Cloud Centre of Excellence provides centralized guidance without blocking speed. It defines approved architectures, security standards, and reusable templates that teams can follow confidently, ensuring consistency across environments while still allowing teams to innovate quickly. - Adopt Policy-as-Code
Embedding governance into CI/CD pipelines ensures security is enforced automatically rather than manually. Policies around tagging, configuration baselines, and resource limits are applied at deployment time, preventing misconfigurations from ever reaching production. - Automate Provisioning and Cleanup
Managing cloud sprawl manually is time-consuming and error-prone. Automation helps identify idle or unused servers, storage, and workloads and clean them up automatically, reducing risk, saving costs, and allowing teams to focus on innovation while maintaining control. - Enforce Tagging and Accountability
Tagging establishes ownership. When every resource is labeled by team, project, and environment, responsibility for cost, security, and cleanup becomes clear, preventing outdated assets and encouraging better cloud hygiene. - Use a Unified Cloud Management or Security Platform
Relying on disconnected tools creates visibility gaps and duplicated effort. A unified platform centralizes asset visibility, posture management, risk prioritization, and compliance, eliminating blind spots across cloud environments. - Regularly Review and Optimize Cloud Usage
Cloud environments evolve rapidly, and resources that were once critical can become idle or oversized. Regular reviews help identify underused instances, unused storage, and over-provisioned workloads, reducing unnecessary costs and limiting the attack surface. - Monitor Shadow IT and SaaS Usage
Unauthorized cloud and SaaS services often go unnoticed until a breach or audit failure occurs. Continuous monitoring helps detect these services early, enabling teams to bring them under governance or safely decommission them. - Align with Cloud Compliance Using Major Benchmarks
Aligning cloud governance with established benchmarks such as CIS, NIST, and HIPAA helps keep environments secure and compliant. Automated detection of misconfigurations and audit-ready reporting allows teams to focus on resolving the risks that matter most.
- Establish a Cloud Centre of Excellence (CCoE)
Overall by addressing cloud sprawl proactively, organizations will create a cloud environment that is efficient, secure, and built to support long-term success.

