Microsoft Open Management Infrastructure (OMI) is an open-source project which allows users to manage configurations across remote and local environments and collect statistics. The primary goal of OMI is to provide a rich, high-performance, standard-based management stack that is suitable for a wide range of management applications. These include cloud management, storage management, server hardware management, device management, and network management. OMI supports most UNIX systems and modern Linux platforms. OMI is used extensively in Azure services like Open Management Suite (OMS), Azure Insights, Azure Automation, Azure Log Analytics, Azure Diagnostics, etc., and comes pre-deployed on Azure VMs as part of the onboarding process. Microsoft has fixed multiple Microsoft OMI Critical Vulnerabilities 2021 which can be done using a patch management tool.
Multiple critical vulnerabilities have been identified in Microsoft Open Management Infrastructure (OMI), allowing an attacker to escalate privileges and execute arbitrary code on the affected system. These vulnerabilities are identified with CVE-2021-38647, CVE-2021-38648, CVE-2021-38645, and CVE-2021-38649. A vulnerability management software can identify and mitigate these vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability Details of Microsoft OMI Critical Vulnerabilities 2021
- CVE-2021-38647: Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution
This vulnerability exists due to a simple conditional statement coding mistake combined with an uninitialized authentication struct. The flaw allows any request without an Authorization header to have privileges to that of the root user. This vulnerability occurs when OMI exposes the HTTPS management port (5986/5985/1270) externally, which is the default configuration for standalone installations and Azure Configuration Management or System Center Operations Manager (SCOM). This vulnerability falls into a “Critical” severity with a CVSS base score of 9.8 (AV:N/AC:L/PR:N/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
- CVE-2021-38648: Local Privilege Escalation
This is similar to CVE-2021-38647: Unauthenticated Remote Code Execution from an exploitation point of view. A low privilege user can remove the Authorization header from the request and execute it as a root user. Due to a different cause for this flaw, security researchers consider it a separate vulnerability. This vulnerability falls into a “High” severity with a CVSS base score of 7.8 (AV:L/AC:L/PR:L/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
-
CVE-2021-38645 – Local Privilege Escalation
This exists due to a use-after-free error which allows an attacker to exploit a race condition and execute code as root. This vulnerability falls into a “High” severity with a CVSS base score of 7.8 (AV:L/AC:L/PR:L/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
- CVE-2021-38649 – Local Privilege Escalation
Security researchers discovered another local privilege escalation vulnerability in Microsoft Open Management Infrastructure (OMI). It falls into the “High” severity category with a CVSS base score of 7.0 (AV:L/AC:H/PR:L/UI:N/S:U/C:H/I:H/A:H).
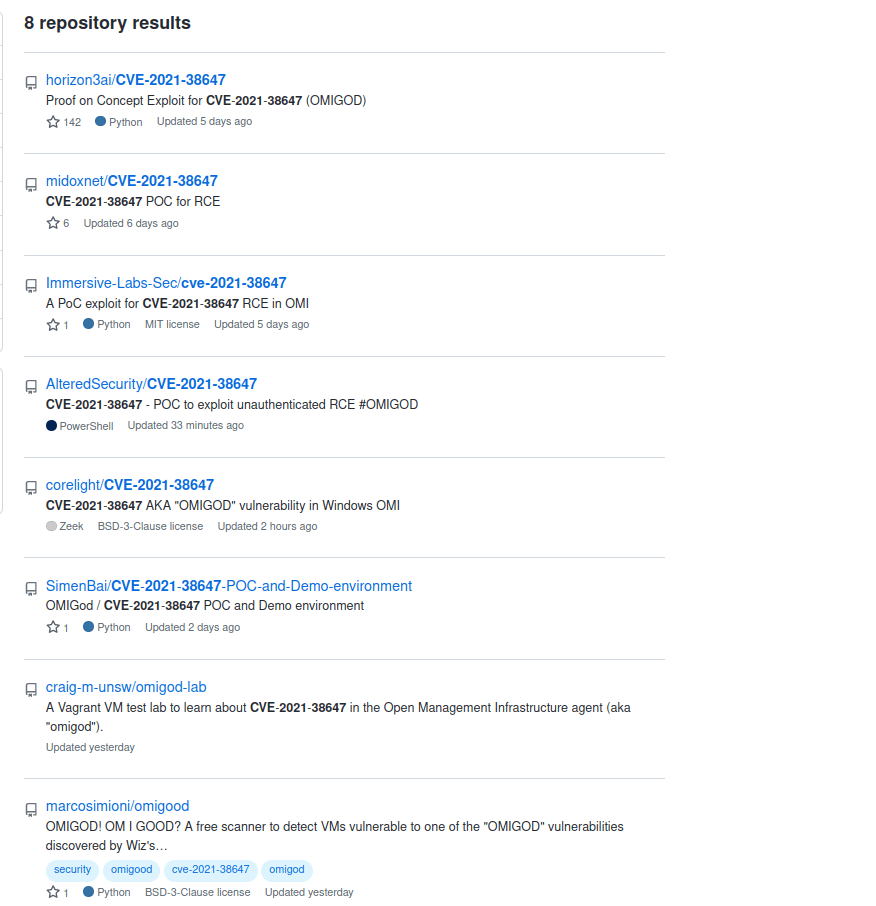
PoC of Microsoft OMI Critical Vulnerabilities 2021
Multiple PoCs are already published for the critical unauthenticated, remote code execution vulnerability. A simple search of CVE in Github fetches us eight results.
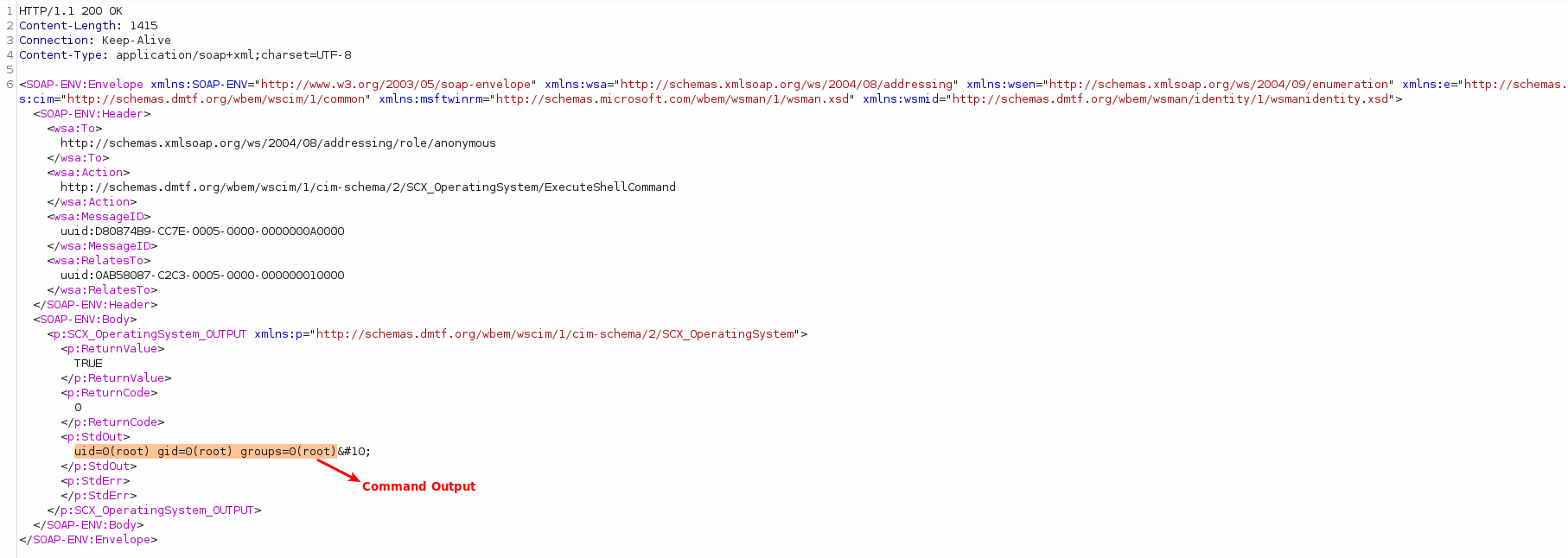
All PoCs send the same HTTP request without an Authorization header to execute arbitrary code with root privileges. However, a typical crafted HTTP request exploiting this RCE vulnerability to run the ‘id‘ command is given below:
Response with an output of the command executed:
CVE-2021-38647 Actively Exploited In The Wild
Finally, As per many researchers, attackers are actively scanning for vulnerable targets for CVE-2021-38647 and installing malware. Mirai botnet is one such threat that has also been found attacking vulnerable Azure Linux OMI endpoints to get into it while closing the ports it exploited to stop other botnets from taking over the system. In addition, several cryptocurrency miner payloads have been seen being deployed in these attacks also.
Affected
All Microsoft Open Management Infrastructure (OMI) versions below v1.6.8-1 are vulnerable. These vulnerabilities affect the following list of products:
- Azure Stack Hub
- Azure Sentinel
- Azure Security Center
- Container Monitoring Solution
- Log Analytics Agent
- Azure Automation Update Management
- Azure Automation State Configuration, DSC Extension
- System Center Operations Manager (SCOM)
- Azure Diagnostics (LAD)
- Azure Open Management Infrastructure
Impact
- Successful exploitation of this vulnerability allows an attacker to gain elevated privileges and execute arbitrary code on the affected system.
Solution
Microsoft OMI Critical Vulnerabilities 2021 are fixed in the latest Microsoft Open Management Infrastructure (OMI) version 1.6.8-1. More details on fixes for other services using OMI can be found here.
However, SanerNow can detect these vulnerabilities. Moreover, it is highly recommended that the affected systems should be patched as soon as possible.