Researchers have discovered a critical remote code execution bug in OpenSMTPD email server. This flaw in OpenSMTPD, OpenBSD email server, is known to be exploitable since May 2018. The vulnerability, tracked as CVE-2020-7247, is exploitable both locally and remotely.
OpenSMTPD is a Unix daemon that implements the Simple Mail Transfer Protocol to deliver messages on a local machine or to relay them to other SMTP servers. OpenSMTPD forms a part of the OpenBSD email server project and is also compatible with other operating systems such as FreeBSD, NetBSD, macOS, and Linux.
Technical Details
Mail servers generally use a mechanism to validate the sender and recipient mail addresses. In OpenSMTPD, function smtp_mailaddr() is responsible for the validation of mail addresses. In smtp_mailaddr()(fig2):
-
- valid_domainpart() is called to validate the domain name of a mail address. This function only accepts IPv4 and IPv6 addresses, and alpha-numeric, ‘.’, ‘-‘, and ‘_’ characters.
- valid_localpart() is called to validate the local part of a mail address. This function only accepts alpha-numeric, ‘.’, and MAILADDR_ALLOWED characters.
MAILADDR_ALLOWED is a white-list adopted as per RFC 5322. MAILADDR_ALLOWED includes “!#$%&’*/?^`{|}~+-=_” characters.
MAILADDR_ESCAPE is another list of characters which includes “!#$%&’*?`{|}~”. If any character from MAILADDR_ESCAPE is encountered in the mail address, it is transformed to “:” character by mda_expand_token() function. This is the process of escaping.
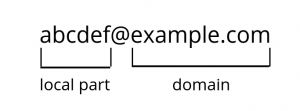 fig1. structure of a mail address
fig1. structure of a mail address

fig2. function smtp_mailaddr()
The presence of smtp_mailaddr() function’s white-listing and the escaping mechanism in mda_expand_token(), help in preventing an attacker from passing dangerous characters to the shell which executes MDA commands. This is very crucial for the security of OpenSMTPD.
A mail delivery agent or message delivery agent (MDA) is responsible for the delivery of e-mail messages to a local recipient’s mailbox. In OpenSMTPD, MDA commands are executed through a shell (in mda_unpriv()) :
execle("/bin/sh", "/bin/sh", "-c", mda_command, (char *)NULL, mda_environ);
The default MDA method here is “mbox”, and the corresponding MDA command in parse.y is :
asprintf(&dispatcher->u.local.command,
"/usr/libexec/mail.local -f %%{mbox.from} %%{user.username}");
In the above command, %{user.username} denotes the local user (local part of the recipient address) and
%{mbox.from} is the sender address. %{mbox.from} or the sender address is under the control of an attacker and can be manipulated to include any code. smtp_mailaddr()’s white-listing(MAILADDR_ALLOWED) and the escaping mechanism in mda_expand_token(), prevent a user from passing dangerous characters to the shell via the sender address.
We can see that the security mechanism is intact. But, the question of how smtp_mailaddr() allows remote code execution(CVE-2020-7247) arises.
The point of error
A simple coding flaw was discovered in smtp_mailaddr() which could allow an attacker to elevate privileges and run arbitrary code. Lets consider a scenario when the domain name of the mail address is empty. In such cases, smtp_mailaddr() adds a default domain name automatically and returns 1. However, on close analysis it can be seen that this function returns 1 even when the local part of the address is invalid(fig2), while it should have returned 0 due to the presence of invalid characters(fig1).
This flaw can be abused by including invalid characters in the mail address. These characters are passed on without validation to the shell which executes the MDA Commands. And thus, code execution can be achieved.
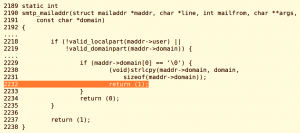 fig3. error in smtp_mailaddr()
fig3. error in smtp_mailaddr()
Although there are a few limitations on the exploitation, security researchers from Qualys have detailed how these limitations can be overcome and a successful exploit can be launched.
For example, an attacker can execute sleep command as a root user as shown below.
 fig4. invalid characters accepted in sender and recipient addresses
fig4. invalid characters accepted in sender and recipient addresses
The limitations for exploitation identified are:
- the maximum length of a local part is 64 characters.
- the characters in MAILADDR_ESCAPE (such as, ‘$’ and ‘|’) get transformed into ‘:’ character.
These limitations were overcome using the technique from Morris worm, the first computer worms distributed via the Internet.
Affected Products
OpenBSD version 6.6
Impact
Successful exploitation allows attackers to run shell commands with root privileges.
Solution
OpenBSD has released patches to mitigate the vulnerability. Apply the latest patches for OpenBSD or upgrade to OpenSMTPD version 6.6.2p1 or later.
We recommend that these patches be installed at the earliest.

