Microsoft has released its May 2025 Patch Tuesday updates, addressing many vulnerabilities across its product lineup. This month’s release tackles 72 flaws, focusing on five zero-day vulnerabilities that are reportedly actively exploited in the wild. Additionally, two other vulnerabilities were publicly disclosed before patches were available, raising concerns about potential exploitation.
The chart below displays the vulnerabilities along with their corresponding enumeration.
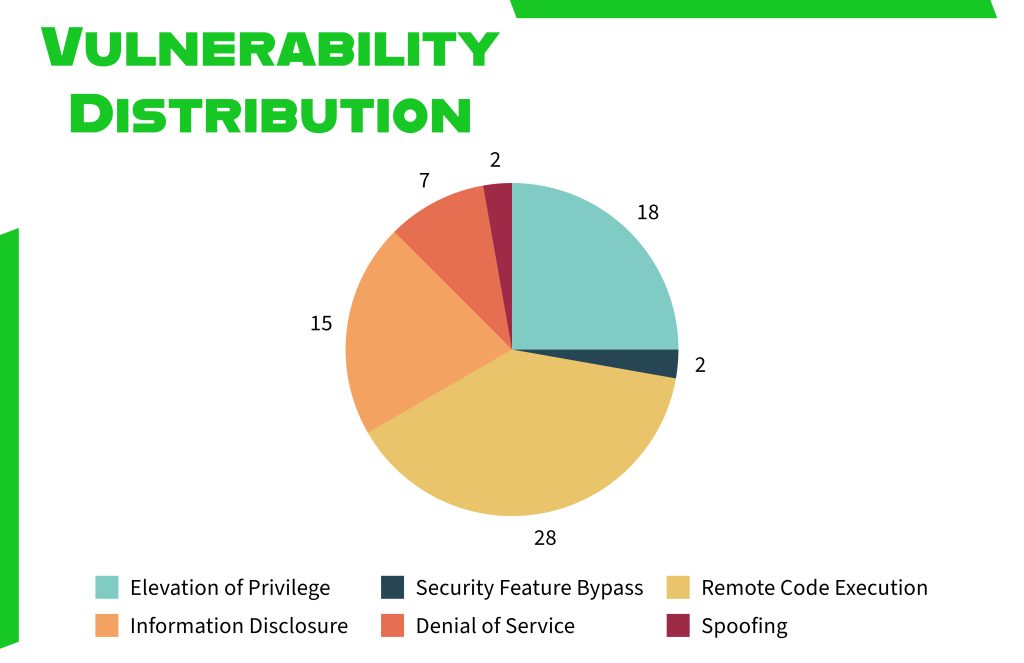
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities Under Active Exploitation
This Patch Tuesday brings fixes for five zero-day vulnerabilities that have been actively exploited, demanding immediate attention from administrators and users. These are:
- CVE-2025-30397 – Scripting Engine Memory Corruption Vulnerability
Details: This vulnerability is a type confusion issue within the scripting engine that occurs when a resource is accessed using an incompatible type. Successful exploitation could enable a remote attacker to execute arbitrary code on an affected system. Attack scenarios typically involve an attacker tricking a user into opening a specially crafted file or visiting a malicious website, possibly using Internet Explorer mode in Microsoft Edge.
CVSS Score: 7.5
Notes: Exploitation requires user interaction.
- CVE-2025-30400 – Microsoft DWM Core Library Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
Details: This flaw is a use-after-free vulnerability in the Windows Desktop Window Manager (DWM) Core Library (dwmcore.dll). A local attacker who successfully leverages this vulnerability could gain SYSTEM-level privileges.
CVSS Score: 7.8
Notes: The vulnerability necessitates local access to the targeted machine.
- CVE-2025-32701 – Windows Common Log File System Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
Details: This is one of two actively exploited elevation of privilege vulnerabilities fixed in the Windows Common Log File System (CLFS) driver this month. An attacker who manages to exploit this flaw could achieve SYSTEM privileges. The standard exploitation method involves a use-after-free condition.
CVSS Score: 7.8
Notes: To exploit this, an attacker would generally need prior access to the system or the ability to execute a specially crafted application.
- CVE-2025-32706 – Windows Common Log File System Driver Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
Details: This is the second actively exploited vulnerability in the CLFS driver detailed in the May 2025 updates. Similar to CVE-2025-32701, successful exploitation grants an attacker SYSTEM privileges. The vulnerability may also stem from improper input validation, leading to a use-after-free scenario.
CVSS Score: 7.8
Notes: It’s emphasized that attackers who exploit these CLFS vulnerabilities can gain complete control to run arbitrary code, install malicious software, or alter data.
- CVE-2025-32709 – Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability
Details: This elevation of privilege vulnerability is present in the Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock (AFD.sys). It is characterized as a use-after-free flaw. An authenticated attacker could exploit this to elevate their privileges to the administrator level.
CVSS Score: 7.8
In Focus: Publicly Disclosed Vulnerabilities
Information on the following two vulnerabilities was publicly available before today’s security patches were issued. While active exploitation was not confirmed at the update release, their public status increases the potential for future attacks.
- CVE-2025-26685 – Microsoft Defender for Identity Spoofing Vulnerability
Details: This vulnerability is due to improper authentication mechanisms within Microsoft Defender for Identity. An unauthenticated attacker on the Local Area Network (LAN) or an adjacent network could exploit this to conduct a spoofing attack.
CVSS Score: 6.5
Notes: For most organizations, automatic updates are expected to address this issue. However, environments where Defender for Identity operates in a disconnected mode or where NTLM has been entirely disabled might require specific review and action.
- CVE-2025-32702 – Visual Studio Remote Code Execution Vulnerability
Details: This is a remote code execution vulnerability impacting Visual Studio. An attacker could exploit this flaw by convincing a user to download and open a malicious file. This action could lead to local code execution via command injection.
CVSS Score: 7.8
Notes: The attack vector is local, meaning the attacker relies on the user interacting with a malicious file on their system. The release information did not specify the source that reported this vulnerability.
Affected Products
Microsoft’s May 2025 security updates encompass a broad range of software and services.
- .NET and Visual Studio (including Build Tools for Visual Studio)
- Active Directory Certificate Services (AD CS)
- Azure
- Azure Automation
- Azure DevOps
- Azure File Sync
- Azure Storage Resource Provider
- Microsoft Brokering File System
- Microsoft Dataverse
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
- Microsoft Defender for Identity
- Microsoft Edge (Chromium-based)
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office Outlook
- Microsoft Office PowerPoint
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft PC Manager
- Microsoft Power Apps
- Microsoft Scripting Engine
- Remote Desktop Gateway Service
- Role: Windows Hyper-V
- Universal Print Management Service
- UrlMon
- Visual Studio
- Visual Studio Code
- Web Threat Defense (WTD.sys)
- Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock
- Windows Common Log File System Driver
- Windows Deployment Services
- Windows Drivers
- Windows DWM
- Windows File Server
- Windows Fundamentals
- Windows Hardware Lab Kit
- Windows Installer
- Windows Kernel
- Windows LDAP – Lightweight Directory Access Protocol
- Windows Media
- Windows NTFS
- Windows Remote Desktop
- Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS)
- Windows Secure Kernel Mode
- Windows SMB
- Windows Trusted Runtime Interface Driver
- Windows Virtual Machine Bus
- Windows Win32K – GRFX
Instantly Fix Risks with SanerNow Patch Management
SanerNow patch management is a continuous, automated, and integrated software that instantly fixes risks exploited in the wild. The software supports major operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS, as well as 550+ third-party applications.
It also allows you to set up a safe testing area to test patches before deploying them in a primary production environment. SanerNow patch management additionally supports a patch rollback feature in case of patch failure or a system malfunction.
Experience the fastest and most accurate patching software here.


