Custom scripting in patching workflow helps organizations to back up the data from getting lost or can be used to upload the already backed data. Few organizations create a complete patch management process using scripts to help maintain the organization’s security posture and cut off the cost of third-party tools. Patch Management Software can resolve these issues.
Though scripting can be beneficial, it can also come with its own set of challenges. Dive in to learn more about the different types of scripting and the challenges of custom scripting. A good patch management tool can be very helpful in this instance.
Different types of patching scripts
1. Post-Remediation Script:
As the name suggests, these scripts are executed after you complete the patch management process. These are generally used to apply all the data which you have collected. For example, you have backed up all the data from a particular application, say MongoDB; after the patching process, you can design a script that can help you to store all the backed-up data files in case you miss any information.
2. Pre-remediation script:
During certain situations, there are cases where an organization would have lost all the information in the process of patching. To avoid them, you can introduce a pre-remediation script that would help you back up the data even before the patching begins.
Challenges of Custom Scripting
Generally, these challenges occur when you try to execute a whole patch management process using scripting without any tools.
1. Complexity:
Developing scripts for the entire patching process is complicated and time-consuming. Instead of developing scripts for the complete patching process, choose a particular set of tasks. For example, you might not need some assets that are running on certain ports to be patched. Introducing scripts during deployment to prevent this can be significantly effective.
2. Maintenance:
Patching workflow changes when new patch management process need immediate attention or if you have encountered a zero-day vulnerability. At that time, custom scripting needs to be updated, and it is necessary for IT admins to always remain up-to-date with the latest patching trends.
3. Security:
Custom scripts may introduce security risks if they are not properly executed. It might introduce vulnerabilities into your patching process.
How does Custom Scripting Work in SanerNow?
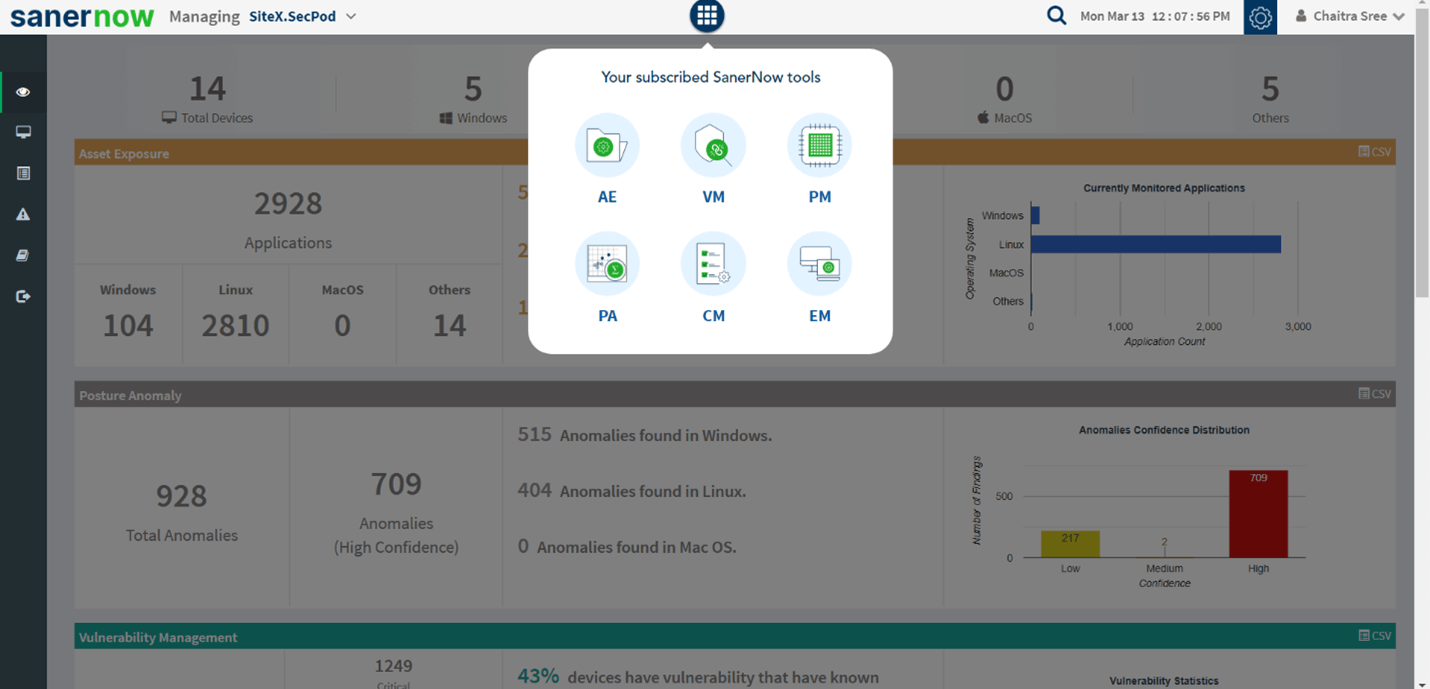
1: Select Patch Management (PM) from the menu.
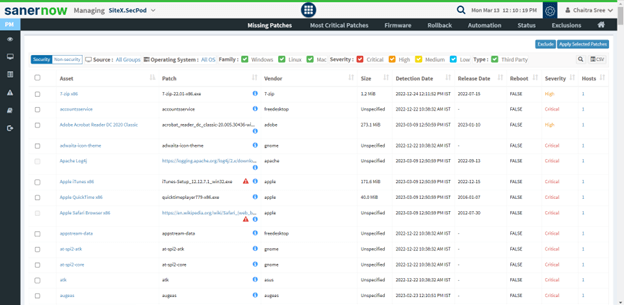
2: Click on the missing patches section. Where you will have a list of available patches for deployment.
3: Choose an application you need to patch and click on the apply patches; you will be prompt with the below window.
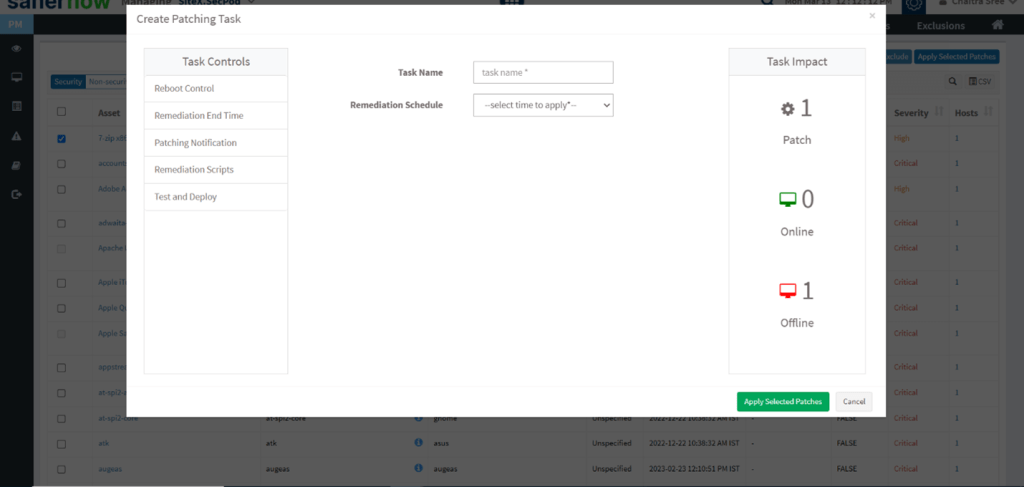
Step 4: Fill in all the information according to your preference, and in order to deploy scripts click on the remediation scripts option. Here, you will be able to deploy .bat, .sh, .deb, .pkg, and more.
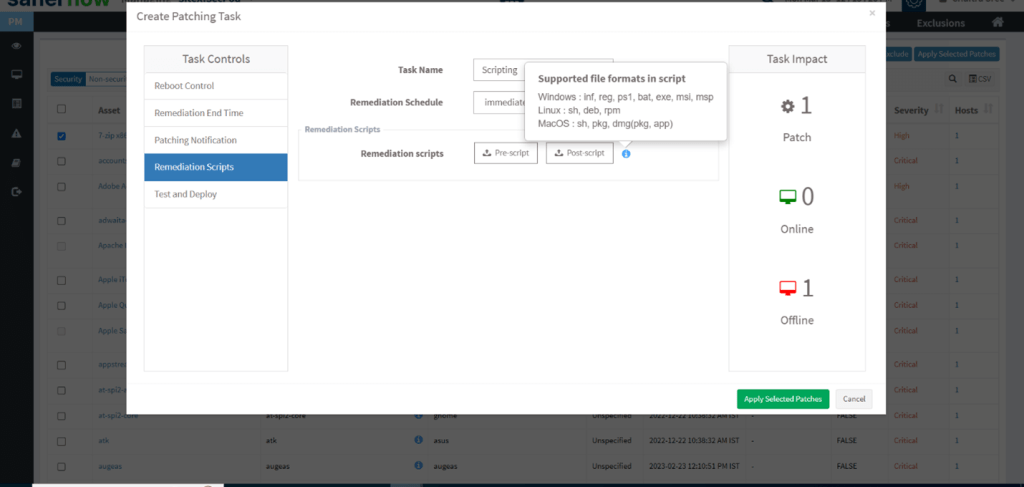
After uploading the script, click Apply on patches, and the patches are ready for deployment.
Custom scripting is easier using SanerNow Patch Management. It is completely automatic and supports patching for all major OSs and 450+ third-party applications. If you have not tried SanerNow yet, opt for its 30-day free trial or book a demo.