It’s time for another Patch Tuesday! This month, Microsoft has released patches for 137 flaws, including 14 critical bugs and one zero-day.
The chart below displays the types of flaws that Microsoft has patched today. Note that it excludes four Mariner and three Edge flaws that were fixed earlier this month.
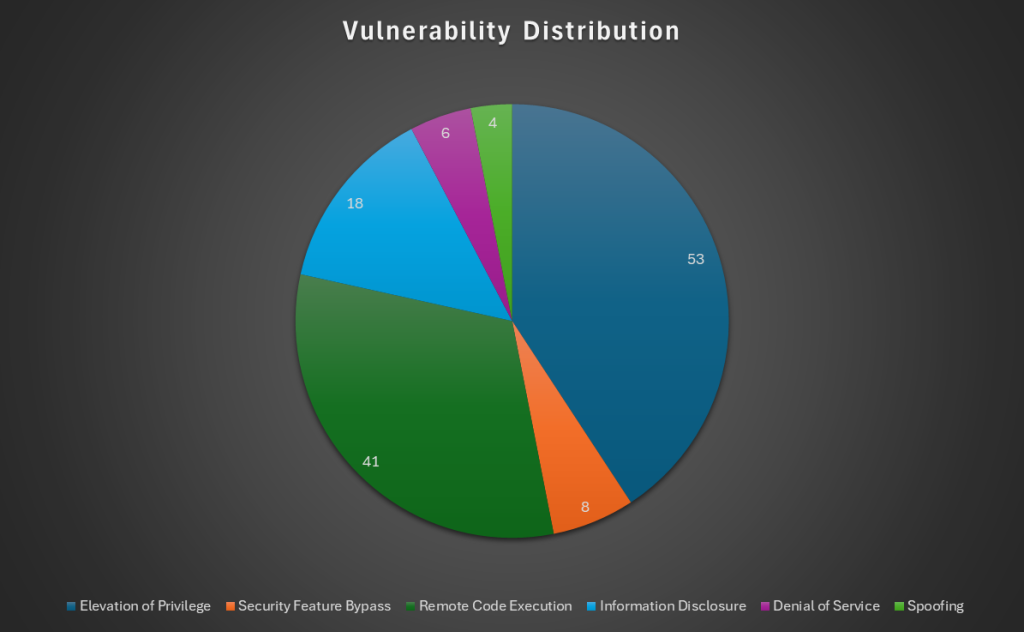
Elevation of Privilege appears to be the most common vulnerability type, covering 38% of the patched flaws, and Remote Code Execution is a close second.
Vulnerability Details
- CVE-2025-49719: The only zero-day to be fixed this month is an Important-severity information disclosure vulnerability in Microsoft SQL Server, assigned a CVSS score 7.5. The flaw stems from insufficient input validation, allowing unauthenticated remote attackers to retrieve sensitive data over a network connection. Although the issue has been publicly disclosed, there is no indication of active exploitation in the wild.
This vulnerability impacts several SQL Server versions, including 2022, 2019, 2017, and 2016. Successful exploitation could expose uninitialized memory, which may leak sensitive information and undermine the confidentiality of affected systems.
CVE-2025-47981: This flaw is a critical-severity remote code execution vulnerability in the Windows SPNEGO Extended Negotiation (NEGOEX) security mechanism, carrying a CVSS score of 9.8. The flaw arises from a heap-based buffer overflow in the NEGOEX component, which unauthenticated remote attackers can exploit to run arbitrary code on the target system. The attack does not require user interaction and is triggered by sending maliciously crafted messages to a vulnerable server.
While SPNEGO (Simple and Protected GSSAPI Negotiation Mechanism) plays a key role in Windows authentication, it is not universally required. Many modern applications—particularly web and cloud-based services—prefer alternative authentication solutions such as OAuth, SAML, or JWT, depending on their security architecture.
CVE-2025-49717: This flaw is a critical RCE vulnerability in Microsoft SQL Server, with a CVSS score of 8.5. It allows authenticated low-privilege users to trigger a heap-based buffer overflow and execute arbitrary code remotely.
Exploitation can lead to a complete escape from SQL Server’s security context, allowing code execution on the host OS. The flaw affects both on-premises and Azure IaaS deployments. Microsoft has released patches for all supported versions (2016–2022) via GDR and CU channels.
Affected Products and Solution
If you have any of the following products installed, update them! Microsoft’s Security Update Guide details mitigations and patches for each vulnerability. You can also use tools to help you apply said patches.
- AMD L1 Data Queue
- AMD Store Queue
- Azure Monitor Agent
- Capability Access Management Service (camsvc)
- HID class driver
- Kernel Streaming WOW Thunk Service Driver
- Microsoft Brokering File System
- Microsoft Configuration Manager
- Microsoft Graphics Component
- Microsoft Input Method Editor (IME)
- Microsoft MPEG-2 Video Extension
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Office Excel
- Microsoft Office PowerPoint
- Microsoft Office SharePoint
- Microsoft Office Word
- Microsoft PC Manager
- Microsoft Teams
- Microsoft Windows QoS scheduler
- Microsoft Windows Search Component
- Office Developer Platform
- Remote Desktop Client
- Role: Windows Hyper-V
- Service Fabric
- SQL Server
- Storage Port Driver
- Universal Print Management Service
- Virtual Hard Disk (VHDX)
- Visual Studio
- Visual Studio Code – Python extension
- Windows Ancillary Function Driver for WinSock
- Windows AppX Deployment Service
- Windows BitLocker
- Windows Connected Devices Platform Service
- Windows Cred SSProvider Protocol
- Windows Cryptographic Services
- Windows Event Tracing
- Windows Fast FAT Driver
- Windows GDI
- Windows Imaging Component
- Windows KDC Proxy Service (KPSSVC)
- Windows Kerberos
- Windows Kernel
- Windows MBT Transport driver
- Windows Media
- Windows Netlogon
- Windows Notification
- Windows NTFS
- Windows Performance Recorder
- Windows Print Spooler Components
- Windows Remote Desktop Licensing Service
- Windows Routing and Remote Access Service (RRAS)
- Windows Secure Kernel Mode
- Windows Shell
- Windows SmartScreen
- Windows SMB
- Windows SPNEGO Extended Negotiation
- Windows SSDP Service
- Windows StateRepository API
- Windows Storage
- Windows Storage VSP Driver
- Windows TCP/IP
- Windows TDX.sys
- Windows Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) Device Host
- Windows Update Service
- Windows User-Mode Driver Framework Host
- Windows Virtualization-Based Security (VBS) Enclave
- Windows Win32K – GRFX
- Windows Win32K – ICOMP
- Workspace Broker

Instantly Fix Risks with Saner Patch Management
Saner patch management is a continuous, automated, and integrated software that instantly fixes risks exploited in the wild. The software supports major operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS, as well as 550+ third-party applications.
It also allows you to set up a safe testing area to test patches before deploying them in a primary production environment. Saner patch management additionally supports a patch rollback feature in case of patch failure or a system malfunction.
Experience the fastest and most accurate patching software here.

